Hafnium (Hf) Sputtering Targets
Shenzhen Sunrise Metal Industry Co.,Ltd
TEL:0086-0755-27185042
Website:http://www.sunriseta.com
E-Mail:sales@sunriseta.com
Specifications
| (2N) 99% Hafnium Sputtering Target | Request | |
| (2N5) 99.5% Hafnium Sputtering Target | Request | |
| (3N) 99.9% Hafnium Sputtering Target | Request | |
| (3N5) 99.95% Hafnium Sputtering Target | Request | |
| (4N) 99.99% Hafnium Sputtering Target | Request | |
| (5N) 99.999% Hafnium Sputtering Target |
Properties
Molecular Weight 178.49 Appearance Silver Melting Point 2227°C Boiling Point 4602°C Density 13.31 g/cm3 Thermal Expansion (25 °C) 5.9 µm·m-1·K-1 Poisson Ratio 0.37 Vickers Hardness 1760 MPa Young's Modulus 78 GPa Tensile Strength N/A Thermal Conductivity 0.230 W/cm/K @ 298.2 K Electronegativity 1.3 Paulings Specific Heat 0.035 Cal/g/K @ 25 °C Heat of Vaporization 155 K-Cal/gm atom at 4602°C
| Molecular Weight | 178.49 |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Silver |
| Melting Point | 2227°C |
| Boiling Point | 4602°C |
| Density | 13.31 g/cm3 |
| Thermal Expansion | (25 °C) 5.9 µm·m-1·K-1 |
| Poisson Ratio | 0.37 |
| Vickers Hardness | 1760 MPa |
| Young's Modulus | 78 GPa |
| Tensile Strength | N/A |
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.230 W/cm/K @ 298.2 K |
| Electronegativity | 1.3 Paulings |
| Specific Heat | 0.035 Cal/g/K @ 25 °C |
| Heat of Vaporization | 155 K-Cal/gm atom at 4602°C |
Material Type Hafnium Symbol Hf Atomic Weight 178.49 Atomic Number 72 Color/Appearance Gray Steel, Metallic Thermal Conductivity 23 W/m.K Melting Point (°C) 2,227 Coefficient of Thermal Expansion 5.9 x 10-6/K
Theoretical Density (g/cc) 13.09 Z Ratio 0.36 Sputter DC Max Power Density
(Watts/Square Inch) 50 Type of Bond Indium Export Control (ECCN) 1C231
| Material Type | Hafnium |
| Symbol | Hf |
| Atomic Weight | 178.49 |
| Atomic Number | 72 |
| Color/Appearance | Gray Steel, Metallic |
| Thermal Conductivity | 23 W/m.K |
| Melting Point (°C) | 2,227 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 5.9 x 10-6/K |
| Theoretical Density (g/cc) | 13.09 |
| Z Ratio | 0.36 |
| Sputter | DC |
| Max Power Density (Watts/Square Inch) | 50 |
| Type of Bond | Indium |
| Export Control (ECCN) | 1C231 |
Z-Factors
Empirical Determination of Z-Factor
Unfortunately, Z Factor and Shear Modulus are not readily available for many materials. In this case, the Z-Factor can also be determined empirically using the following method:
- Deposit material until Crystal Life is near 50%, or near the end of life, whichever is sooner.
- Place a new substrate adjacent to the used quartz sensor.
- Set QCM Density to the calibrated value; Tooling to 100%
- Zero thickness
- Deposit approximately 1000 to 5000 A of material on the substrate.
- Use a profilometer or interferometer to measure the actual substrate film thickness.
- Adjust the Z Factor of the instrument until the correct thickness reading is shown.
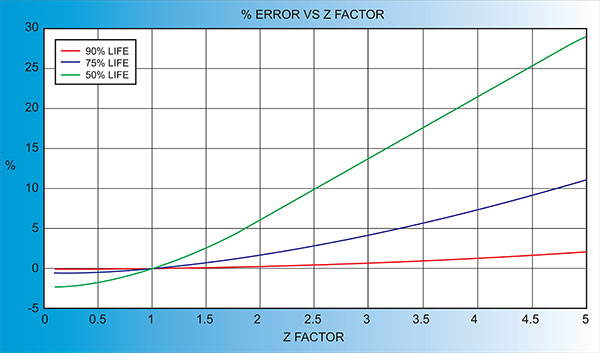
Another alternative is to change crystals frequently and ignore the error. The graph below shows the % Error in Rate/Thickness from using the wrong Z Factor. For a crystal with 90% life, the error is negligible for even large errors in the programmed versus actual Z Factor.
NOTE: This is an Export Controlled Material. Restrictions may apply.

















没有评论:
发表评论